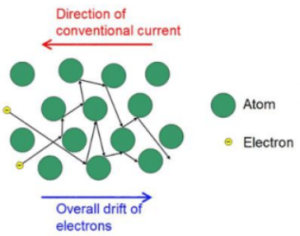
Current
- Current and charge must be conserved item.
- The current is the amount of charge per second [latex]I = \frac{ \Delta Q}{ \Delta t}[/latex]
- units: C/s = A
- Direction of current is direction of positive charges’ motion
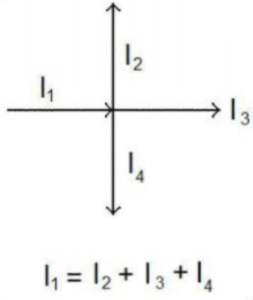
Kirchhoff’s Rules (Or “How to analyze a circuit”)
- The amount of current going into a junction must equal the amount going out (otherwise it would pile up)
- The changes in potential around any closed loop is zero
Circuit Elements
Batteries
- The potential drop across a battery is fixed
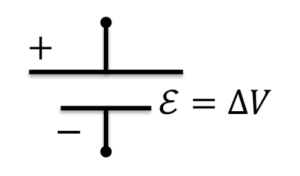
Resistors
- Resistors dissipate electrical potential energy into something else (heat, motion, light, etc.)
- The potential drop across a resistor is related to the current and resistance
[latex]\Delta V = IR[/latex]
- The resistance is fixed by the material, units:
[latex]\frac{V}{A} = \Omega[/latex]
- The potential drop across a wire is zero ([latex]R = 0[/latex])
Capacitors
- A capacitor is two pieces of metal that don’t touch
- Capacitors store charges separated. Therefore, they store energy
- The capacitance is a property of the geometry of the plates
- The potential drop across a capacitor is related to the charge and the capacitance:
[latex]C = \frac{Q}{\Delta V}[/latex]
- For parallel plates
[latex]C_{\parallel} = \varepsilon \frac{A}{d}[/latex]
- Units
[latex]\frac{C}{V} = F[/latex]
Power
- The power provided/stored/dissipated by a circuit element is
[latex]P = IV[/latex]
- Must do element-by-element

